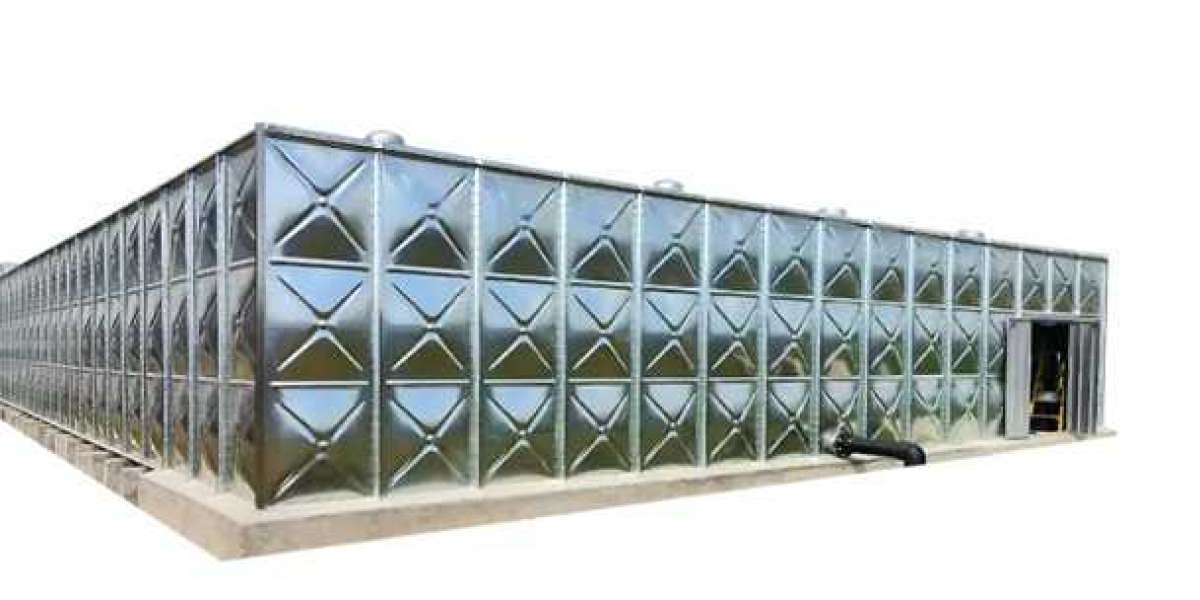
Hot-dip galvanized (HDG) bolted water tanks have good corrosion resistance and still have certain corrosion resistance in harsh environments, especially marine climates and chemical corrosion areas. Hot-dip galvanizing is an anti-corrosion technology that forms a zinc coating by immersing steel parts in molten zinc liquid. The zinc coating provides effective protection for the base steel and can prevent oxidation and corrosion.
In marine climate conditions, salt and humid environment in seawater are the main corrosion factors. The zinc coating can form a dense protective film that can effectively resist salt spray erosion, thereby extending the service life of the bolted water tank. Especially in mild marine climates, the anti-corrosion performance of hot-dip galvanized coatings is particularly outstanding. However, in extremely humid environments or exposed to high concentrations of salt spray, the zinc layer may gradually wear and require regular maintenance and inspection.
In chemical corrosion areas, especially when exposed to acids, alkalis or other corrosive substances, HDG coatings can also provide certain protection, but their tolerance is limited. In corrosive environments such as strong acids and alkalis, the zinc coating may be quickly consumed, so its corrosion resistance is poor. To enhance corrosion resistance, stronger anti-corrosion measures may be required, such as coating protection or the selection of more corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel.
In general, HDG bolted water tanks have good anti-corrosion effects in marine climates and chemical corrosion areas, but their durability is affected by environmental factors. In extreme or persistent corrosive environments, regular maintenance and necessary enhancement measures are the key to ensuring their long-term use.