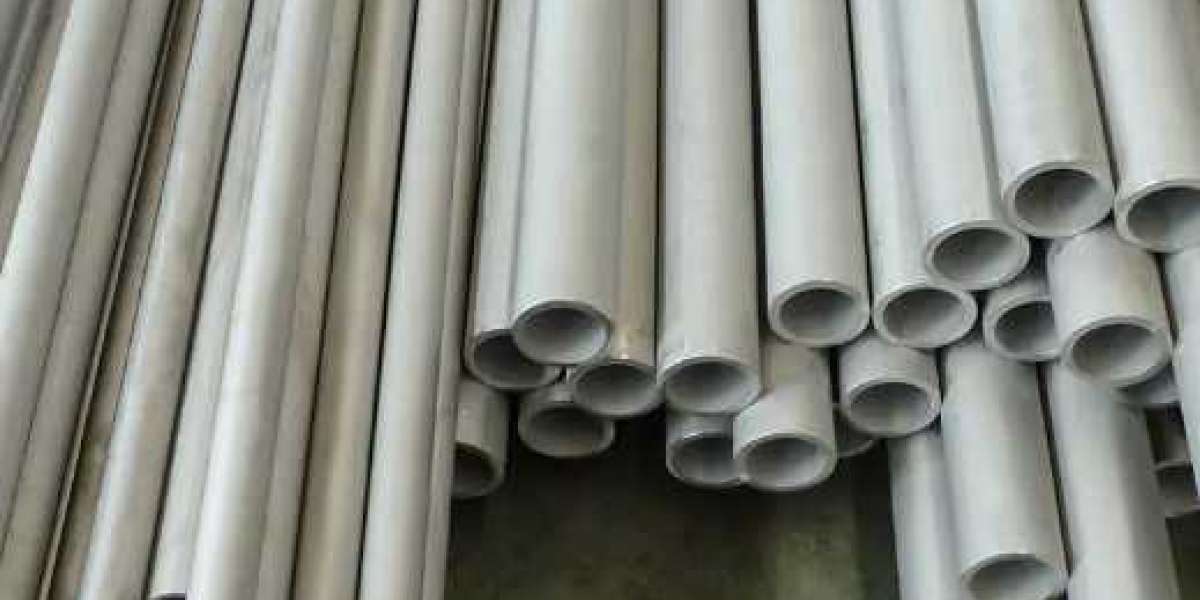
Austenitic stainless steel seamless pipes are widely used in many fields such as petroleum, natural gas, chemical industry, and food processing due to their excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and good mechanical properties. However, their manufacturing process is complex and has many technical difficulties. This article will analyze in detail the manufacturing process and technical difficulties of austenitic stainless steel seamless pipes.
1. Manufacturing process
The manufacturing process of mainly includes the following steps:
Smelting and ingot casting
Smelting: Arc furnace smelting is used as the basic means to accurately control the temperature and furnace atmosphere with arc high temperature to promote the perfect fusion of various alloy raw materials. Argon oxygen decarburization (AOD) and vacuum deoxidation and decarburization (VOD) are used for further refining to reduce the carbon content and accurately control the oxidation of elements such as chromium, so as to obtain low-carbon, low-impurity, and precise composition stainless steel.
Ingot casting: The smelted molten steel is cast into ingots to prepare for subsequent processing.
Hot rolling and hot extrusion
Heating: The ingot is heated to a suitable temperature to improve its plasticity.
Piercing: The solid steel billet is perforated into a tube billet by a piercing machine.
Rolling or extrusion: After three-roller oblique rolling, continuous rolling or extrusion, the tube billet is further processed into a seamless steel pipe.
Cooling and straightening: The steel pipe after rolling or extrusion is cooled and straightened to ensure its dimensional accuracy and shape.
Cold drawing and cold rolling
Annealing: The steel pipe after hot rolling or hot extrusion is annealed to eliminate stress and improve its plasticity.
Pickling: Remove the oxide scale and dirt on the surface of the steel pipe.
Cold drawing or cold rolling: Through multiple cold drawing or cold rolling processes, the wall thickness and diameter of the steel pipe are further reduced to improve its accuracy and surface quality.
Heat treatment: The steel pipe after cold drawing or cold rolling is heat treated to improve its mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
Inspection and warehousing
Hydrostatic test: The steel pipe is subjected to a hydrostatic test to check its sealing and strength.
Flaw detection: Use non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic and eddy current to check whether there are defects inside the steel pipe.
Marking and warehousing: Mark qualified steel pipes and store them in the warehouse.
2. Analysis of technical difficulties
Due to its high strength characteristics, austenitic stainless steel will produce significant tangential stress and plastic deformation during the cutting process, resulting in increased cutting force. Its poor thermal conductivity causes the cutting temperature to rise sharply, accelerating the wear of the tool.
Austenitic stainless steel shows a significant tendency to work hardening during the cutting process, and the degree of hardening is often several times that of ordinary carbon steel. This increases the difficulty of cutting and shortens the life of the tool.
The chips of austenitic stainless steel are strong and the cutting temperature is high, which can easily cause sticking and welding, and damage the surface roughness of the processed parts.
Because austenitic stainless steel contains high melting point elements and high plasticity, coupled with the extremely high temperature generated during the cutting process, the tool wear rate is accelerated, the frequency of sharpening and tool replacement is increased, and production efficiency is affected.
In the manufacturing process of austenitic stainless steel seamless pipes, the parameters of each process need to be strictly controlled to ensure its dimensional accuracy and surface quality. In particular, the cold drawing and cold rolling processes have extremely high requirements for the wall thickness and diameter of the steel pipe.
The price of austenitic stainless steel raw materials is relatively high, and the tool loss during processing is large, resulting in an increase in manufacturing costs. Therefore, how to reduce costs while ensuring quality is an important issue that manufacturers need to face.
3. Countermeasures
Select tools specifically used for processing stainless steel or high-temperature alloys, such as carbide tools and cubic boron nitride (CBN) blades, to improve cutting efficiency and tool life.
Reduce cutting temperature and tool wear by reducing cutting line speed and feed speed, and using appropriate cutting fluid.
Strengthen cooling and lubrication during cutting to reduce cutting temperature and friction, thereby extending tool life and improving processing quality.
Strictly control the process parameters of each process, such as heating temperature, rolling force, cold drawing pass, etc., to ensure the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the steel pipe.
Advanced water pressure test and non-destructive testing technology are used to conduct comprehensive inspections on steel pipes to ensure their quality and safety.
The manufacturing process of austenitic stainless steel seamless pipes is complex and has many technical difficulties. By selecting high-performance tools, optimizing cutting parameters, strengthening cooling and lubrication, strictly controlling process parameters, and adopting advanced testing technology, these technical difficulties can be effectively addressed and production efficiency and product quality can be improved.